As the seasons of carols and the ringing of New Year echoes in the air, reflection and renewal rises with a sharpened desire to move ahead with purpose. This season brings an opportunity for brands to move beyond the noise of festive promotions and step into the world of purpose marketing, a strategic declaration of their brand’s intentions running deeper than a one-off donation or an obligatory CSR drive.
Today’s consumers, especially the younger lot are more discerning as they read and observe brands like books. They look for values, consistency and a mission they can attach their loyalty to. When a brand’s purpose aligns with their own, advocacy follows almost instinctively. Festivities like Christmas and New Year engagements in this sense become a seasonal checkpoint. It is a stage when people reset goals and reconsider their beliefs and support towards social causes. Those brands that choose to step onto this stage, do a lot more than discounts, they align purpose marketing initiatives through donations, employee giving, community engagement and cause-related campaigns that invite consumers to co-creates, making participation a form of persuasion.
Why Purpose Marketing Wins?
Across the world, corporations are rewriting their playbooks with strategies that reflect their new understanding that purpose is power. For example, Mastercard’s pledge to bring 1 billion people into the digital economy by 2050 or Intel’s commitment to ensure 40% women in technical roles by 2030 are not acts of goodwill alone, but a long sighted strategic move to strengthen the brand’s purpose while accelerating social justice, inclusion and sustainability.
Furthermore the governments, investors and consumers now expect brands to uphold more than profits, resulting in corporate social responsibility intersecting with purpose not as a parallel consent but as mutually reinforcing forces.
Benefits of Purpose Marketing :
- Stronger brand equity and long-term differentiation
Purpose marketing comes with a 360 degree approach where it builds an integral relationship with brands and consumers. Purpose-driven brands make a strong impression on consumers, making them remember the brands, trust them and stay for the long term while on the other hand, the “purpose premium” framework, as per to Deloitte, shows that brands with clear purpose enjoy advantages in brand and reputation, sales, innovation, operational efficiency, talent retention and risk mitigation.
- Higher employee morale and retention through meaningful engagement
Employees feel a deeper allegiance to their organisations when they see them championing causes they personally value. When corporate social responsibility is woven into a company’s purpose, it becomes a quiet but powerful force strengthening loyalty and reducing attrition. In an article, Joan Steinberg, Morgan Stanley’s Global Head of Philanthropy quotes,
“it’s just not consumers who expect the company to be a good neighbor. It’s also employees”.

- Greater consumer advocacy driven by authentic purpose
In the era of doing beyond profit, customers want brands to make tangible social impact. A purpose marketing driven approach through CSR approach or cause related marketing enables the consumers to build trust and emotional loyalty. Through credible storytelling showcasing impact, transparency and brand’s ongoing commitment, socially conscious consumers stick for long term, rather than transactional interactions, which further turns them into loyal advocates for the brand, who shall co-steer cause marketing initiatives through interventions like donations at checkout.
- A measurable contribution to SDGs and national development priorities
As India works toward achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by 2030, it is crucial to recognise the power of collective engagement. Purpose marketing- whether through CSR commitments or cause-related initiatives, can become a true gamechanger by activating society’s collective consciousness. When brands align with social causes, they help enable quality education for children from underserved communities, deliver last-mile healthcare to remote regions and empower women, young girls and youth with livelihoods, that allow them to sustain themselves and shape a stronger future.

Giving Back in Action
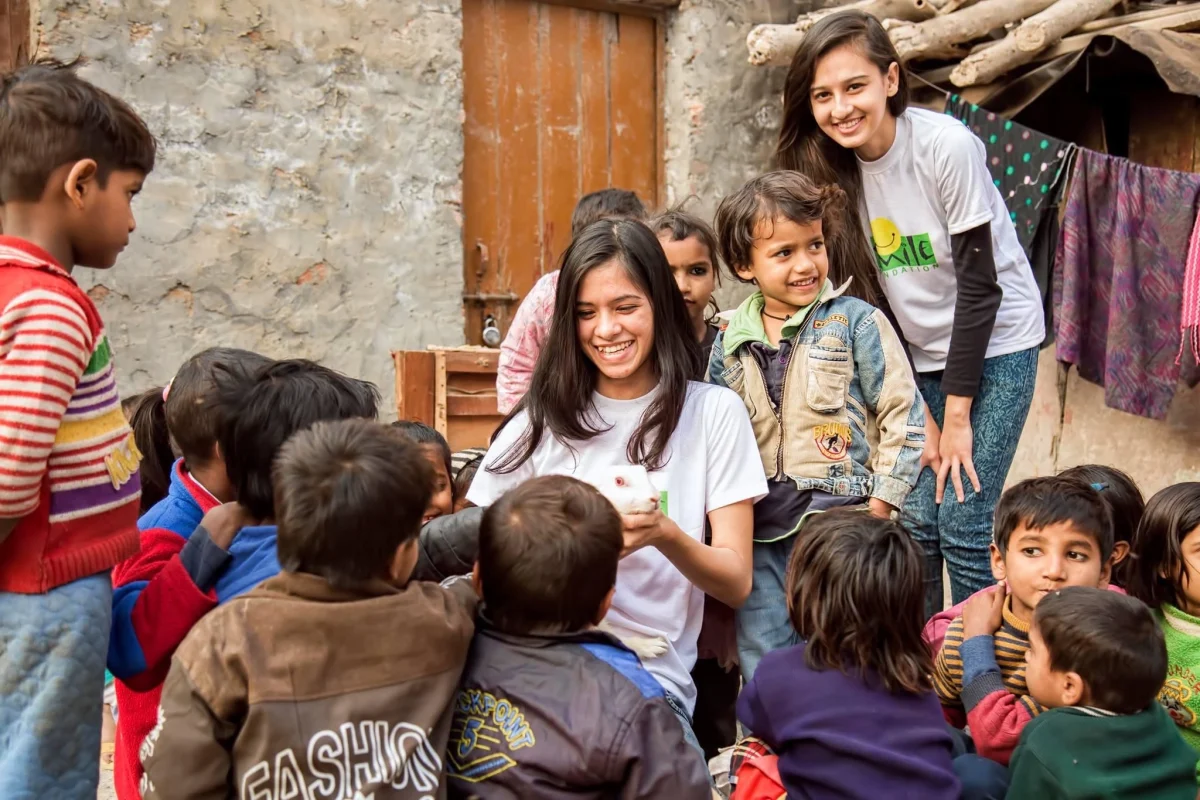
Purpose marketing becomes truly powerful when it shifts from intention to meaningful action. Across India, brands partnering with Smile Foundation have shown how CSR initiatives and cause-related marketing can create real, measurable impact. These collaborations have enabled children from underserved communities to access quality education, delivered last-mile healthcare to remote regions and opened livelihood opportunities for women and youth. In doing so, purpose-driven CSR and CRM interventions have not only strengthened communities but also enhanced brand trust, loyalty and long-term value- proving that when brands invest in purpose, both society and the business grow together.
Smile Foundation’s Purpose Marketing Activities- Case study
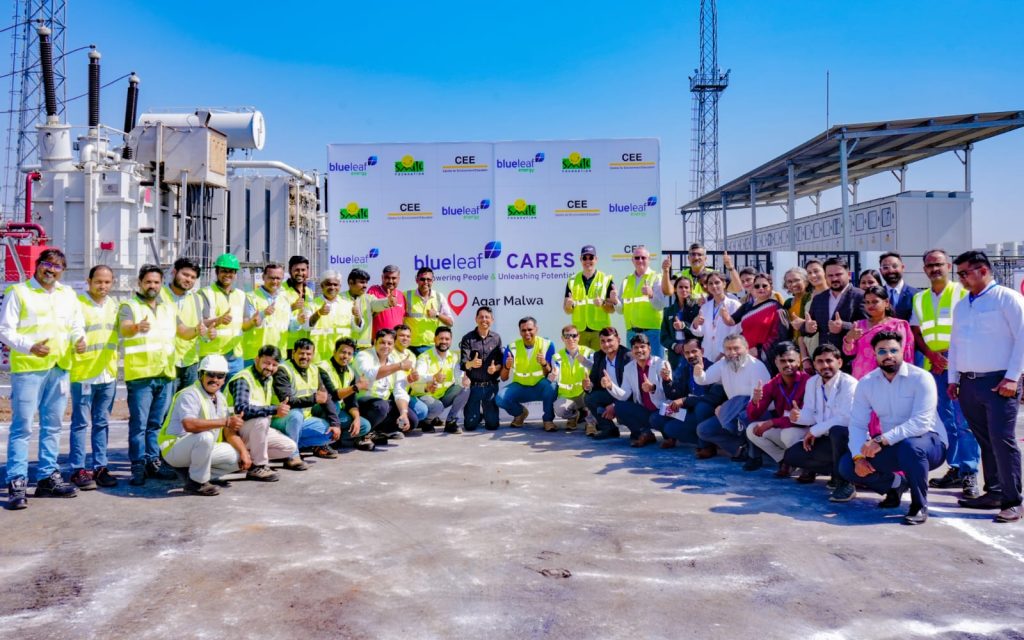

Blueleaf’s Integrated Rural Development Impact
Blueleaf Energy, through its Blueleaf Cares programme, has partnered with Smile Foundation to drive integrated rural development across 27 villages in Madhya Pradesh. Focusing on healthcare, education, livelihoods and the environment, the initiative supports over 10,000 people, while strengthening local systems through community partnerships and alignment with national schemes.
Submarine Pens Turns every Pen into Purpose
Submarine Pens has partnered with Smile Foundation to advance education and healthcare for children across more than 2,000 villages and urban settlements in India. Through this collaboration, the brand integrates social impact into its core identity, turning every pen sold into a meaningful contribution towards stronger, more equitable community outcomes.
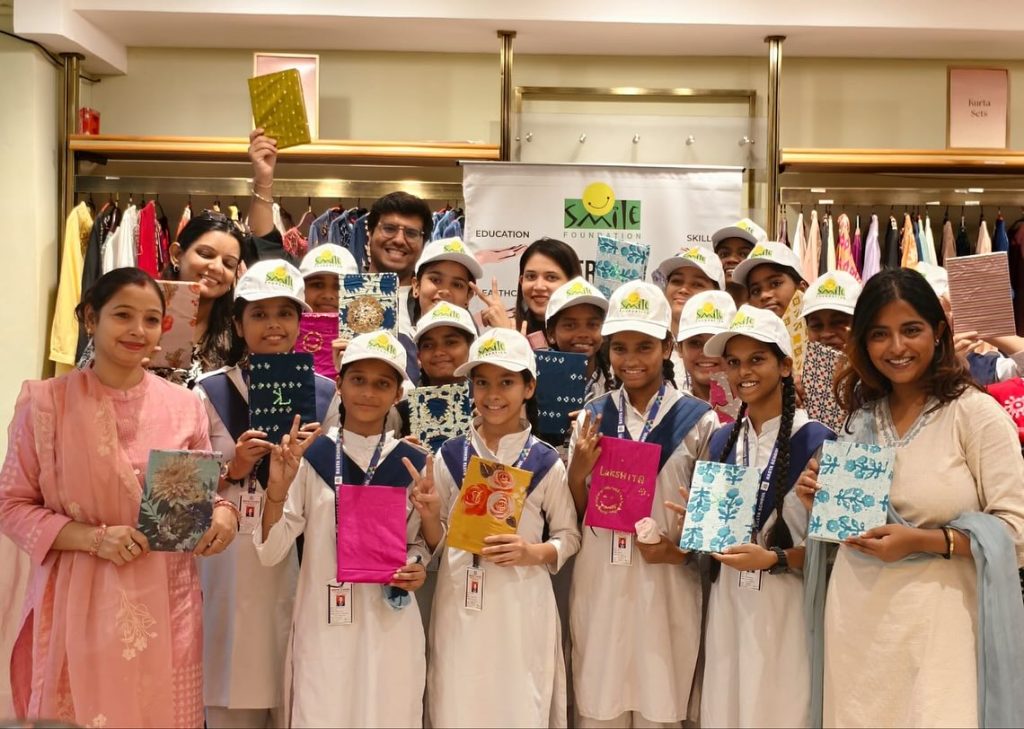

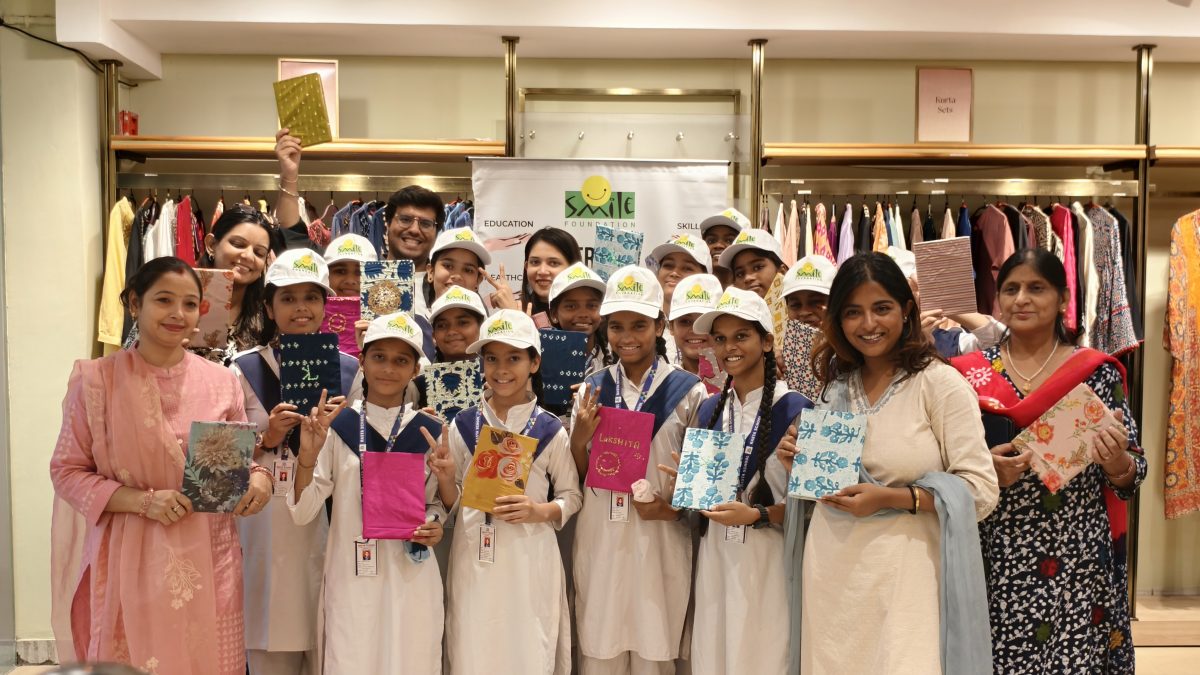
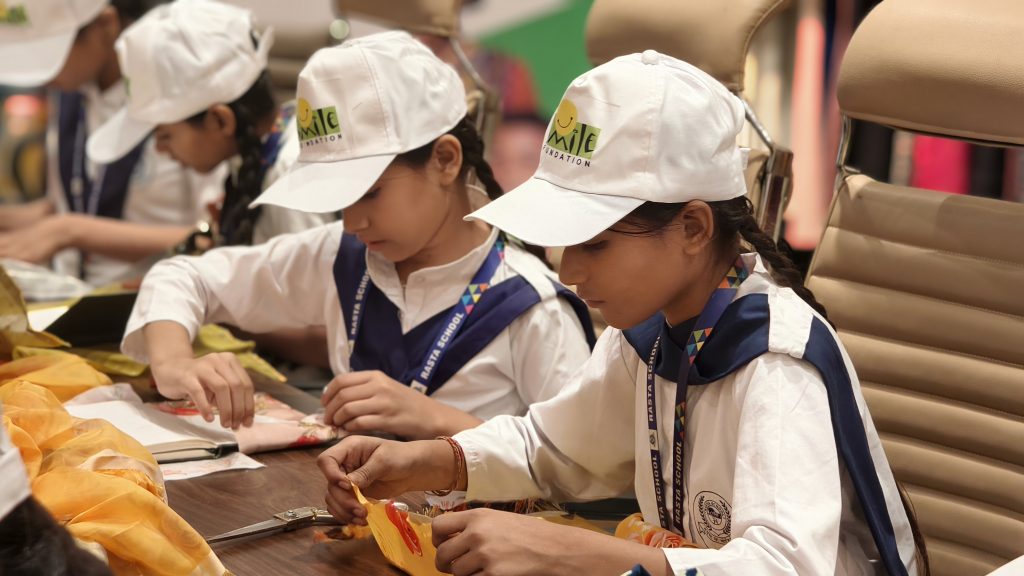
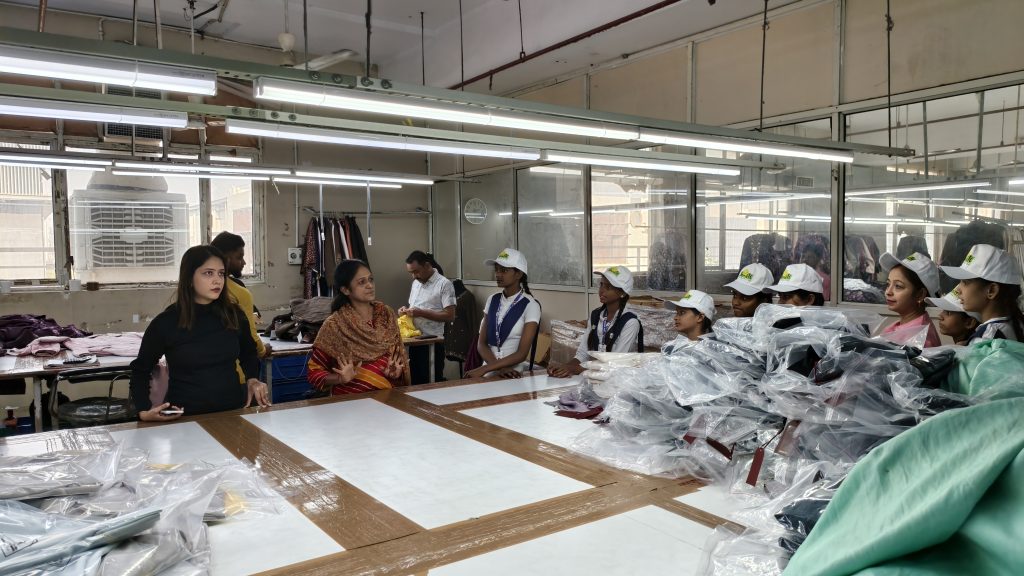
Lakshita’s Creative to Empowerment
Children’s Day became a powerful expression of purpose marketing as Lakshita, in collaboration with Smile Foundation, invited young girls to explore sustainable fashion through hands-on creativity. The event transformed simple crafting into an experience of confidence, imagination and empowerment, while aligning brand values with meaningful social engagement; this celebration demonstrated how purposeful initiatives can spark joy while stitching aspirations for a brighter, more inclusive future.
Indus insights Purpose on Wheels for School going children
Indus Insights’ Manager’s Forum partnered with Smile Foundation to deliver bicycles to children who walk long distances to school- an employee giving programme that was rooted in the spirit of purposeful brand engagement. As volunteers assembled the bikes, children observed, learned and participated, creating a shared moment of joy. This impactful collaboration demonstrated how purpose-led initiatives can strengthen organisational culture, while creating meaningful community value.
Dear Diary’s Purpose-Driven Partnership
Smile Foundation’s collaboration with Dear Diary by Rashmika Mandanna brings the “Kindness Economy” to life through purpose marketing- with part of every sale going towards supporting education of children from the marginalised sections of the country. This initiative shows how brands can embed purpose into products, creating value that goes beyond fragrance to nurture dreams and spark ripples of positive change across communities.
Make New Year of Meaningful Impact with Smile
Businesses today are moving beyond profit to embrace purpose and support causes that strengthen the social fabric of our communities. What was once an optional charitable gesture has now become a core asset, resonating with consumers, employees and communities while advancing business objectives.
Festive moments like Christmas and New Year offer ideal opportunities for brands to transform seasonal campaigns into sustained, purpose-driven initiatives. Whether through CSR interventions, employee engagement programmes or cause-marketing campaigns, companies that embrace purpose position themselves as social pioneers. They foster emotional equity, create meaningful social impact and shape their brands, businesses and markets into catalysts for social good.
Partner with us to integrate purpose into your brand strategy today. Participate with communities, engage your employees and design initiatives that deliver measurable market growth and meaningful social change.
Sources:
- Why Giving Back Increases Brand Loyalty
- 81% of millennials want companies to be good corporate citizens
- Why Smart Companies Give Back
Ways to Promote Your Business With Charitable Marketing
Why a purpose-driven strategy is good for business