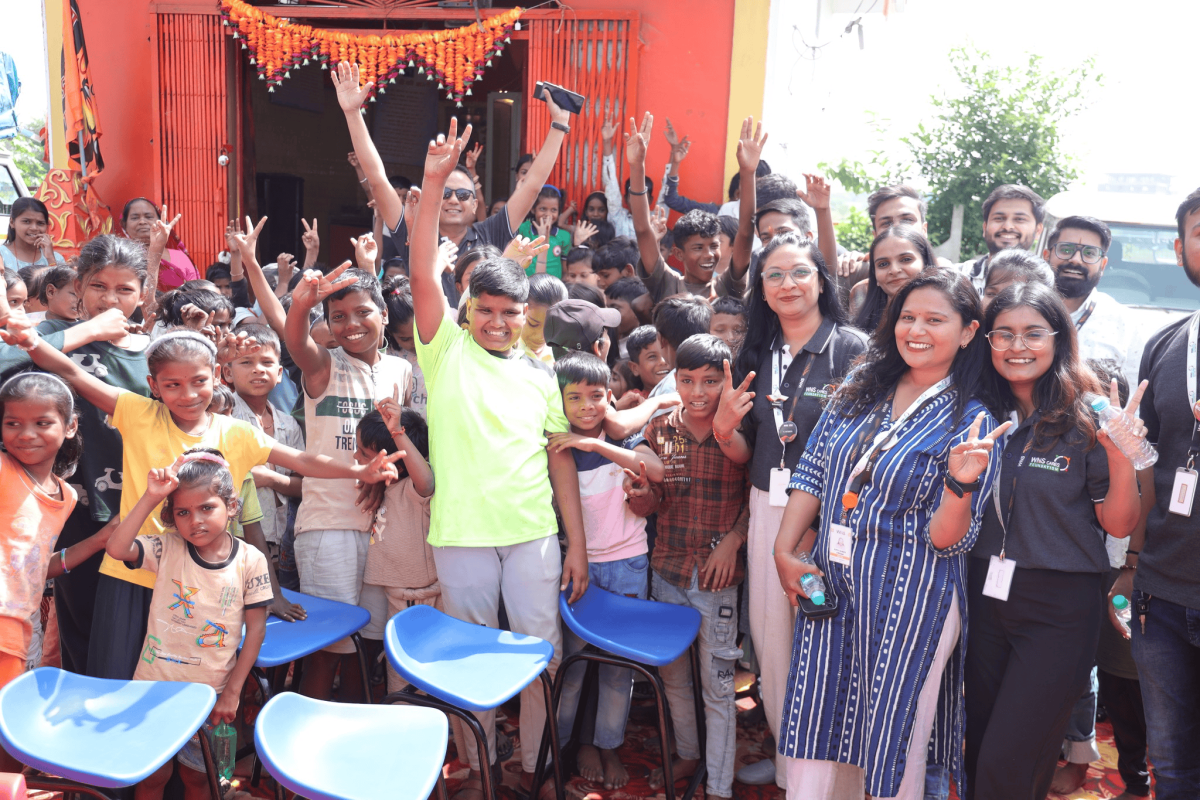
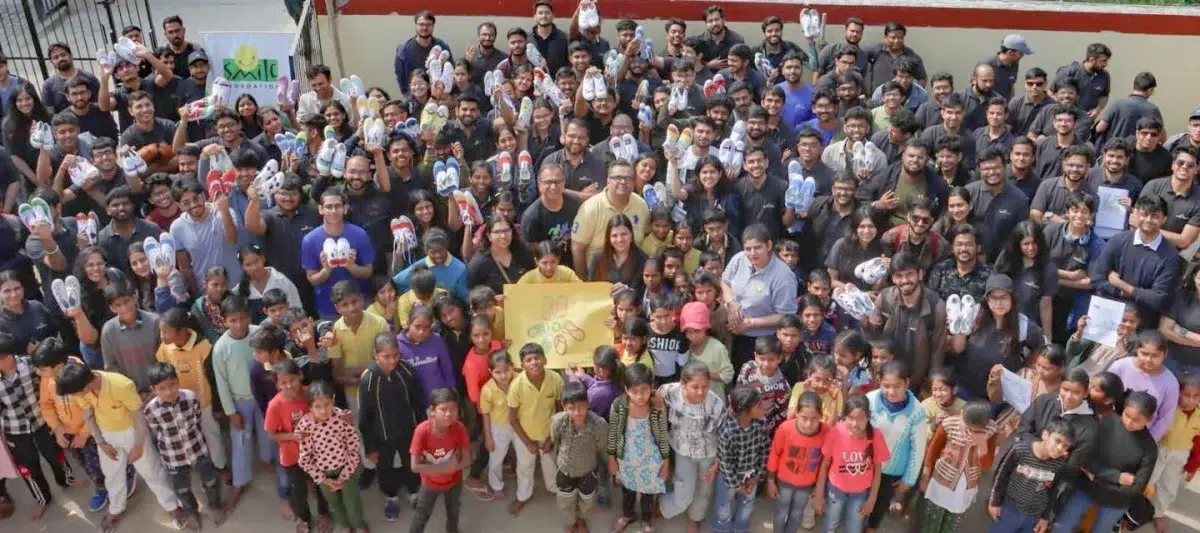
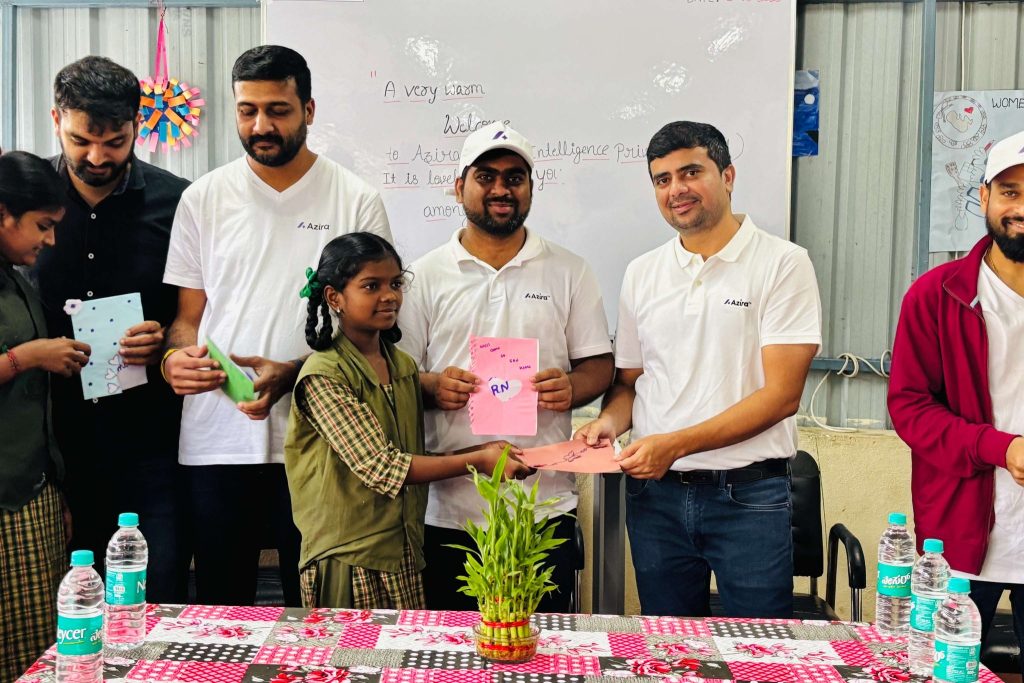
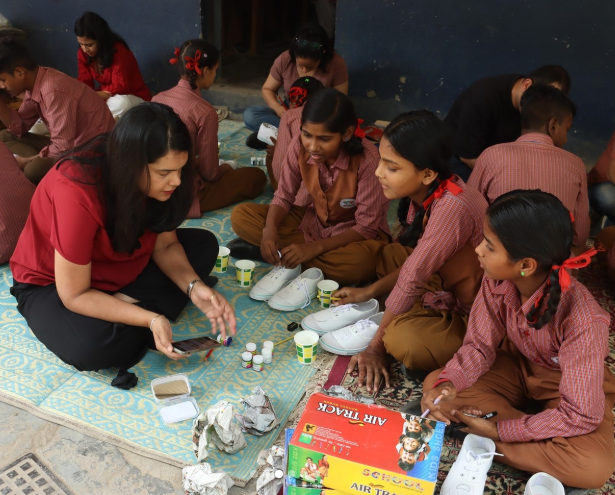
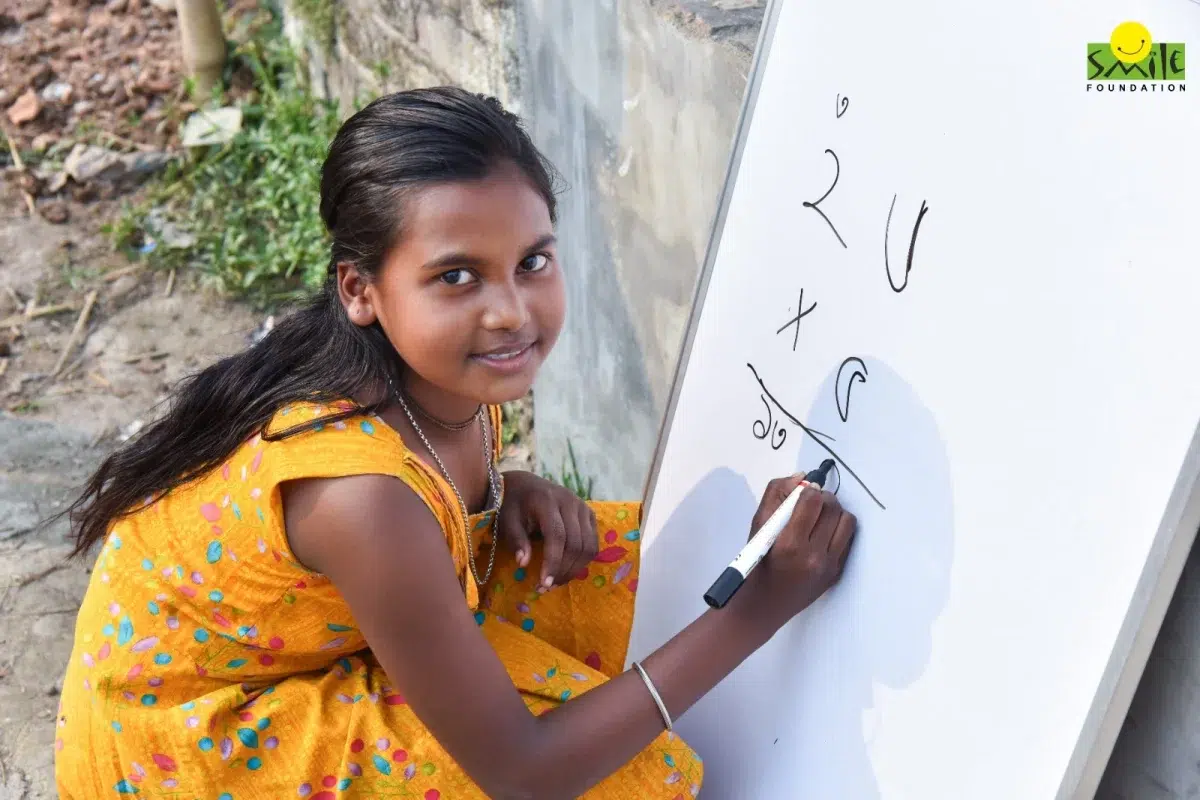When Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) was introduced in India in 2013, it sparked debate. Some hailed it as a vital lever to ensure inclusive national progress, while others dismissed it as a bureaucratic obligation. Fast forward to 2025 and CSR has evolved from a peripheral compliance exercise into a strategic imperative. Today, both large and small enterprises weave CSR into the very fabric of their business, pursuing a shared vision: advancing the nation, one life at a time.
This evolution has not happened in isolation. The rise of CSR-NGO partnerships has become a defining feature of India’s CSR landscape, transforming charitable giving into a measurable force for social change. As ESG commitments gain prominence, corporates and NGOs emerge as dual energies, driving inclusive growth and community transformation.
The Power of CSR-NGO Partnerships
Corporates and NGOs are in many ways polar opposites. Their operational philosophies , priorities and approaches diverge sharply. Yet, precisely this divergence gives rise to extraordinary synergy as when aligned, they become formidable forces, capable of delivering structured and long lasting social impact.
- Enhanced Social Impact
NGOs bring hyperlocal insights and deep community ties, enabling corporates to design initiatives that are both relevant and scalable. By harnessing this expertise, CSR programs address the unique challenges of India’s diverse communities, reaching underserved populations with precision.
- Shared Resources and Risk Mitigation
Pooling financial, human and technical resources makes CSR-NGO partnerships more robust and sustainable. Risks, whether operational or financial are distributed allowing bold,ambitious projects that might otherwise remain unattempted.
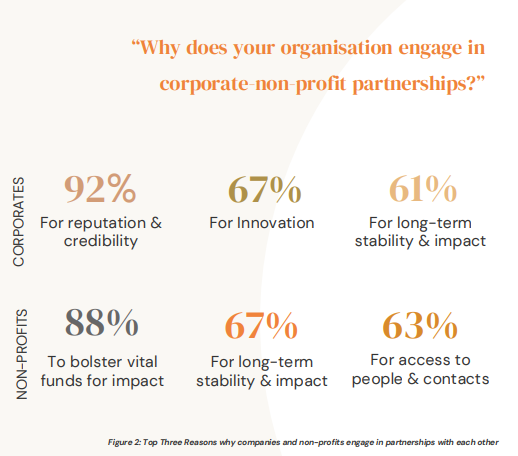
- Strengthening Corporate Reputation
Collaborating with credible NGOs signals authenticity, elevating the corporate brand while reinforcing public trust. Companies are no longer seen as mere profit seekers, they are now recognised and held accountable, as social stakeholders shaping an inclusive world.
- Innovation and Mutual Learning
The contrasting strengths of corporates and NGOs such as financial and managerial expertise v/s grassroots knowledge and closeness, create fragile ground for mutual learning. This exchange fosters continuous improvement, strategic refinement and creative problem-solving, enhancing the effectiveness of interventions over time.
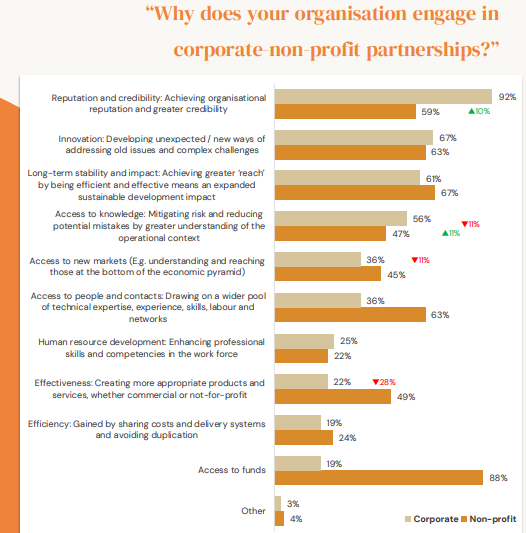
The Strategic Shift in India’s CSR
India’s CSR law mandates that companies dedicate a minimum 2% of net profits to social causes. Initially, this created a transactional dynamic as corporates sought reputational benefits, while NGOs primarily sought funding.
However, times have changed. Modern CSR is no longer about compliance; it is about strategic collaboration. A recent C&E advisory report highlights that companies and non-profit organisations, increasingly join forces now to tackle complex social challenges. Today CSR-NGO partnerships aim not merely to satisfy legal obligations, but to co-create sustainable impact for the communities in which they operate.
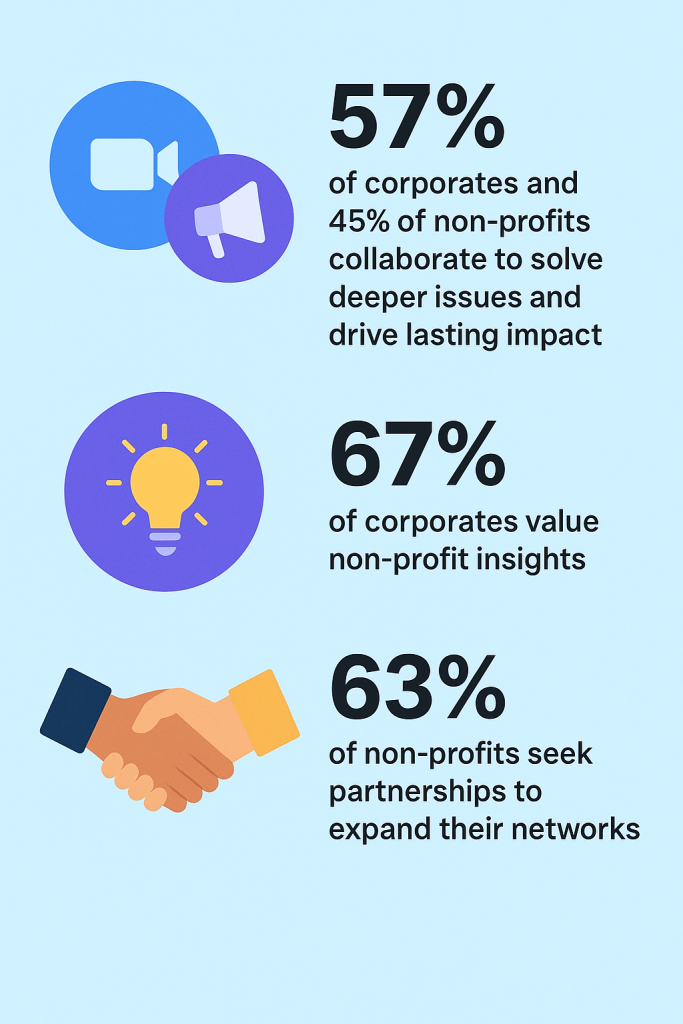
The New CSR Playbook: Data, Tech, Community
- Tech-Enabled CSR
Digital transformation has revolutionised CSR, turning technology into a lever for measurable social outcomes. AI-driven EdTech, digital classrooms, STEM mobile labs, mobile health units, teleconsultations, and real-time screenings are enabling corporates and NGOs to deliver targeted interventions. What was once goodwill has become precision-driven action.
- Measuring Impact with Data
Analytics and impact measurement tools allow CSR interventions to move beyond activity-based metrics to tangible outcomes. Dashboards and real time analytics enhance transparency, accountability and adaptability, enabling corporates and NGOs to track progress and build trust within the communities they serve.
- Building Sustainable and Green Communities
CSR initiatives now embrace environmental stewardship as a core objective. From vegetable gardens and plantation drives to creative “best out of waste” corporate volunteering activities– such partnerships help in integrating the “E” in the ESG, fostering a sustainable ecosystem while infusing the spirit of belongingness in the community.
- Empowering Human Capital
Skill development, inclusive education and financial literacy are at the heart of CSR-NGO partnerships. Digital classrooms, vocational training and microenterprise support especially for women of rural and urban poor communities of India are pivotal for India’s growth. Such interventions help in translating potential into opportunity, bridging social and economic gaps, while creating sustainable livelihoods.
CSR in Action: Real-World Transformations
- Job-Ready Youth: A Pathway to Inclusive Growth

A partnership between Flipkart Foundation and Smile Foundation is transforming the lives of marginalised youth in Bangalore and Hyderabad. Through industry-relevant training in the Banking, Financial Services, and Insurance (BFSI) sector, over 1,000 young individuals have acquired the skills, confidence, and pathways to meaningful employment, demonstrating the tangible impact of CSR-NGO partnerships.
2. Upskilling for Empowerment
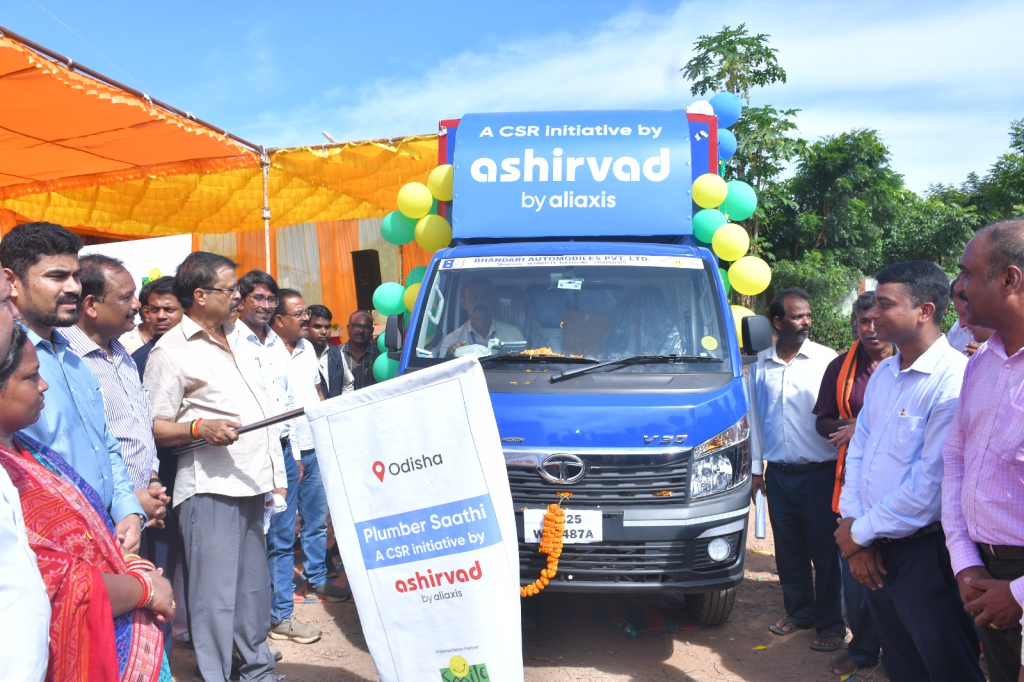

Ashirvad by Aliaxis and Smile Foundation have launched the “Plumber Saathi” mobile training programme across Odisha, equipping youth with practical plumbing skills. By combining corporate expertise with grassroots outreach, the programme promotes self-reliance and contributes to long-term socio-economic development in underserved communities.
3. Strengthening Early Education
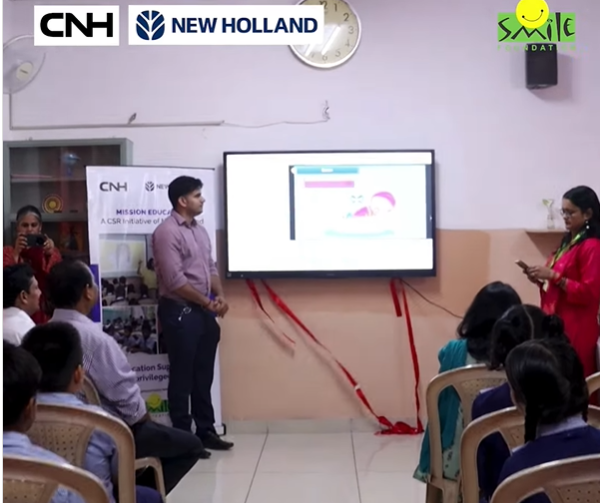

CNH Industrial (New Holland) and Smile Foundation have collaborated to integrate digital classrooms, teacher training, and practical learning tools, addressing foundational gaps in early education. Through interactive technologies, children gain essential literacy and numeracy skills, ensuring equitable learning opportunities and fostering lifelong educational engagement.
Smile Foundation’s CSR Philosophy
India’s CSR landscape has evolved from compliance-driven charity to strategic measurable impact and Smile Foundation embodies this philosophy; supporting those in need by leveraging the expertise of CSR-NGO partnerships for achieving a bigger goal of creating sustainable change, empowering communities and fostering an egalitarian nation.
By combining technology, data and grassroots expertise, Smile Foundation works towards ensuring that collectively both corporates and NGOs in India, become a strategic force for irrevocable positive transformation.
Join us and explore how your orgnaisation can transform goodwill into measurable chance and build a future where every life thrives.
Sources-
- The Impact of Digital Transformation on CSR: Trends, Challenges, and Future Outlook
- Do data-driven CSR initiatives improve CSR performance? The importance of big data analytics capability
- ‘Incredibly resilient’: Corporate-NGO tie-ups switch from ‘tactical’ to ‘problem solving’
- Corporate- Non Profit Partnerships Barometer 2025 by c&e advisory