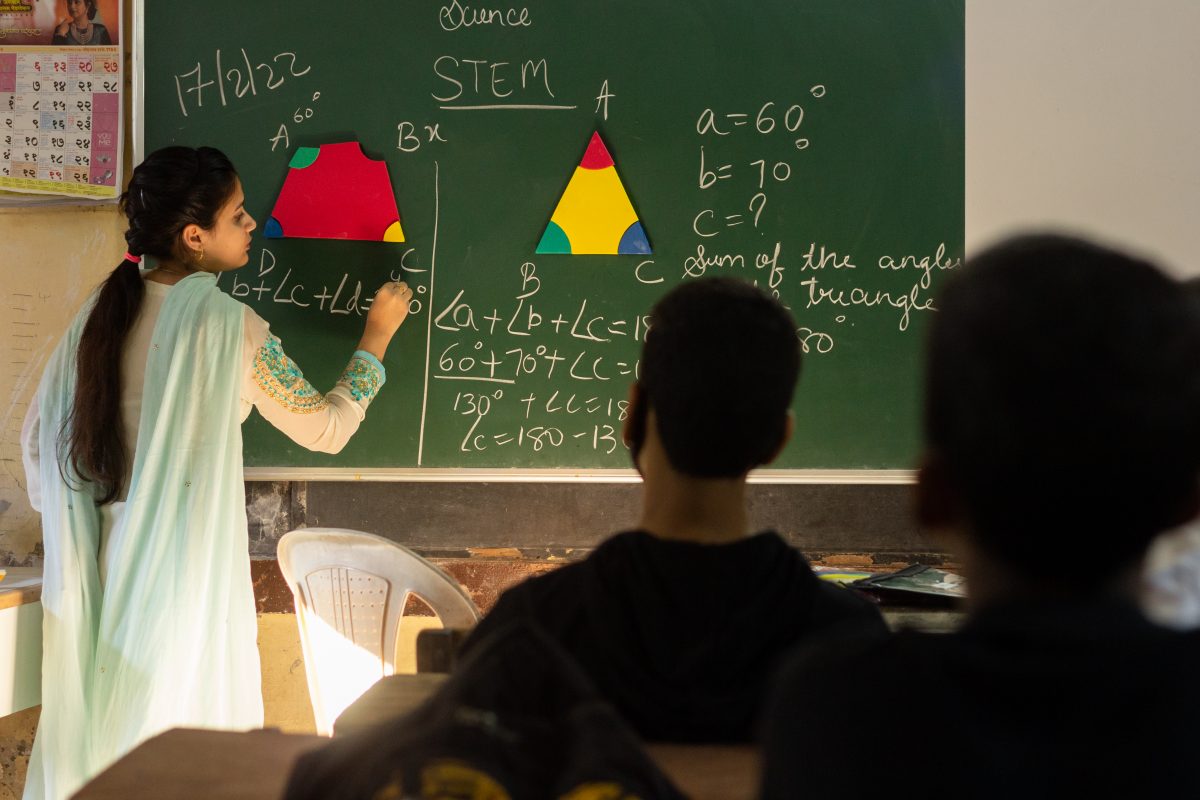Every year World Science Day reminds us that science is the bridge between knowledge and opportunity. From waking up and switching on the lights to discovering life on another planet, the evolution of science shows that when it is blended with digitalisation, it becomes a force that helps the society to grow, heal and sustain itself collectively. In India, science has moved beyond laboratories and has integrated into the daily functionalities of life, like life without it never existed.
To truly celebrate Science Day, we must recognise that science can only drive progress when it is inclusive. When every child, regardless of gender or geography has access to learn, explore and innovate.

Science For Inclusive Future
Science is universal and till the time this is not implemented and adapted in its entirety, we shall be risking losing countless potential innovators and problem solvers.
Smile Foundation for over decades has been working with grassroot communities to bridge the gaps of science education for children belonging to the marginalised communities of India. By creating equitable access for scientific learning and promoting STEM education, our interventions have been working within these communities through capacity building, digital innovation and community engagement to empower the next generation of teachers and engineers.
1. Training and Capacity Building
Regular teacher development workshops strengthen STEM pedagogy, introduce digital tools and enhance classroom leadership. A strong emphasis on gender sensitivity helps teachers identify and correct unconscious biases, ensuring girls receive equal encouragement in scientific learning.
2. Technology-enabled Teaching
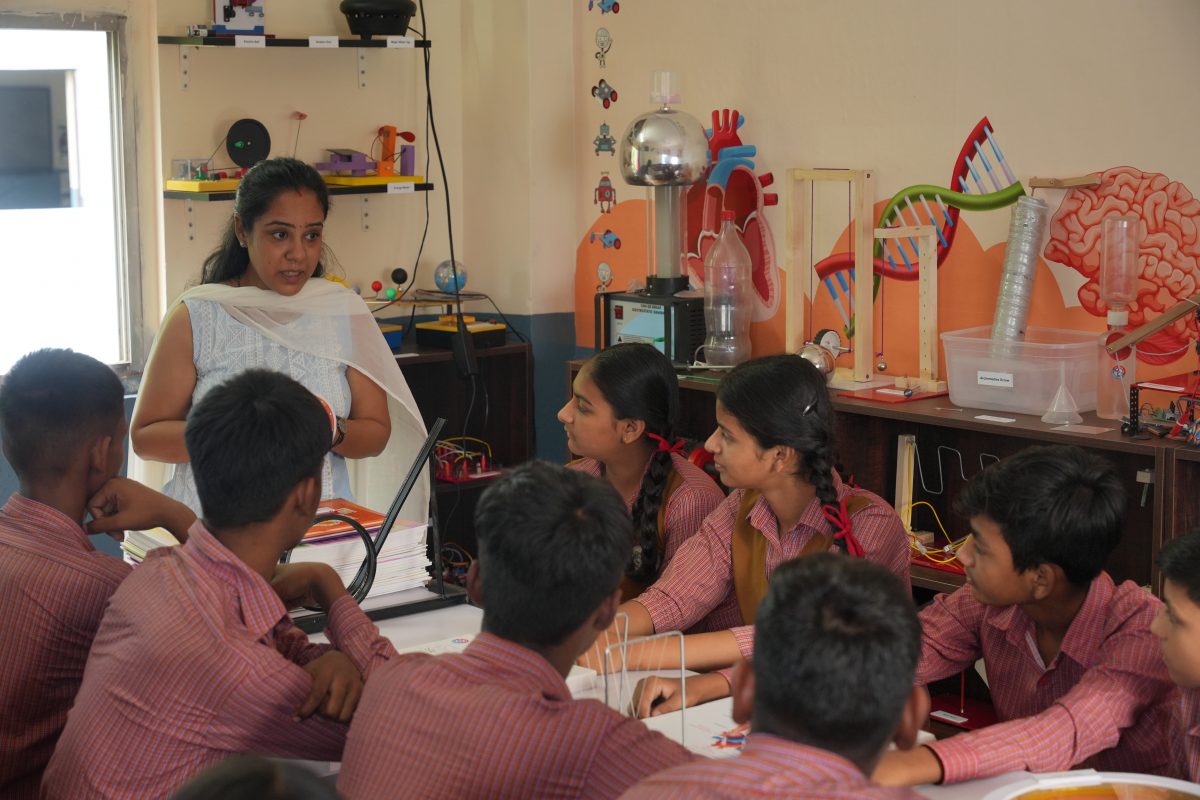
In remote areas, solar-powered digital classrooms have transformed the learning experience. Teachers, especially women, now use visual tools and multimedia lessons to explain complex scientific concepts with confidence and clarity. These innovations make science accessible and engaging for rural learners.
3. Community Sensitisation
Through parent–teacher meetings and outreach sessions, Smile Foundation builds awareness about the importance of science education for girls. This effort has led to tangible results with higher attendance rates, delayed marriage ages and more girls continuing their education beyond primary levels.
The aim is to create a pipeline of empowerment, from student to teacher to role models. Science becomes a source of learning that inspires generational change in how children, especially girls interested in science perceive the subject.
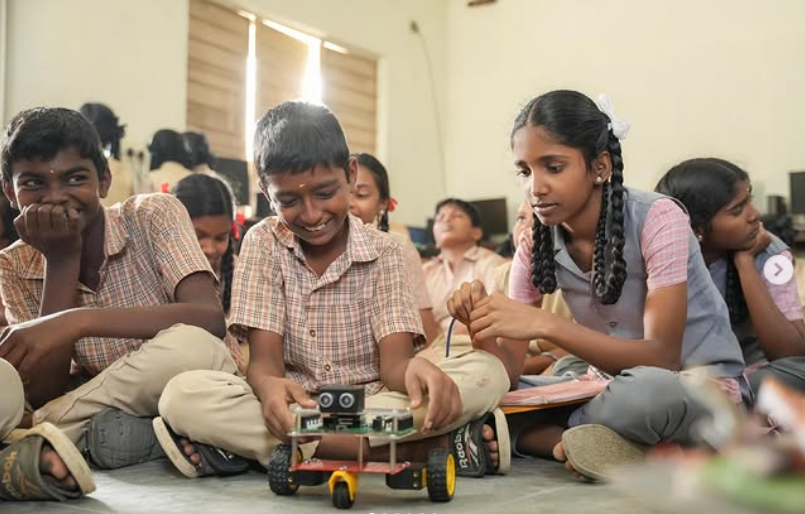

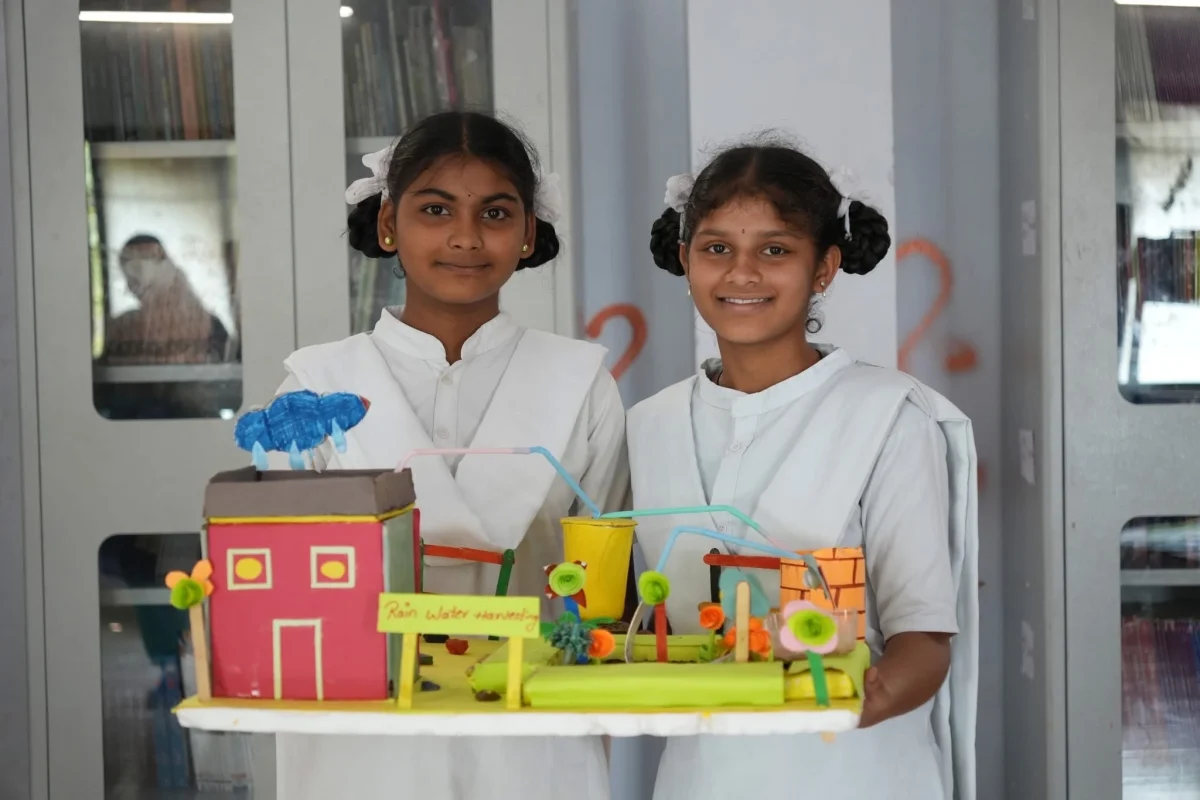
Today STEM learning has become an engaging and enjoyable experience for children through Smile Foundation’s STEM Labs. Here students explore science, technology, engineering and mathematics in simple, hands-on ways. Through interactive activities and guided lessons, they grasp complex concepts with ease, find joy in learning and build confidence to discover something new each day.
Building Sustainable with Scholarships for Girls
According to India Skills report 2025 only 54.81 % of graduates meet industry employability standards. Between 2013-2014 female enrolment in undergraduate programmes rose by 46% and 55.5% at the post graduate level. However, there has been a decline in the enrolment of girls in engineering course by 1.35% at the undergraduate level, whereas at postgraduate level the decline is of 43%.
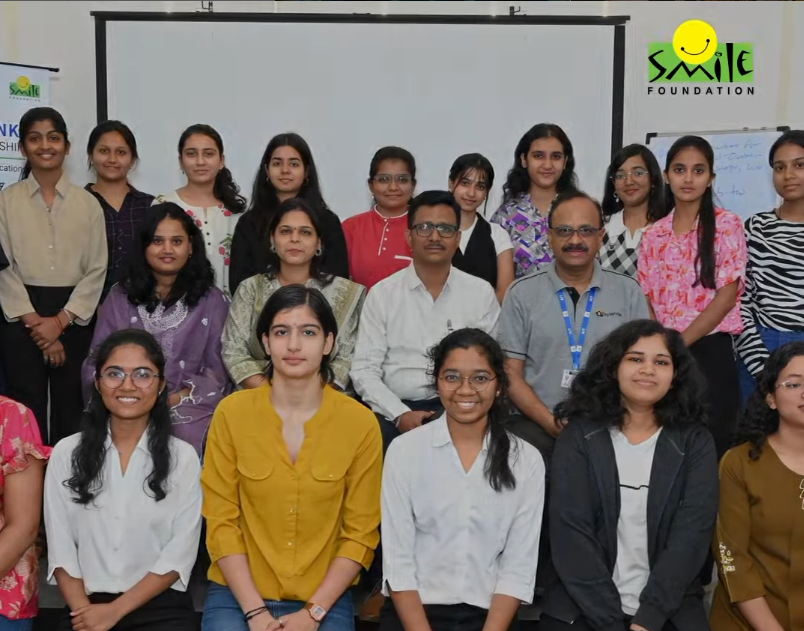

Many first generation college students, especially girls, face more than financial hardships. They have to navigate new challenges like understanding academic culture, professional networking and career opportunities. Traditional scholarships often come with its limitations which usually only aids in accessing engineering courses, but doesn’t support in allowing the student to survive the course and successfully establish themselves as work ready engineers.
Smile Foundation’s Scholarship programme for Girl Engineer adopts a holistic model that combines financial aid with-
- Life skill and digital training
- English fluency session
- Career counselling and mentorship
- Mental health support
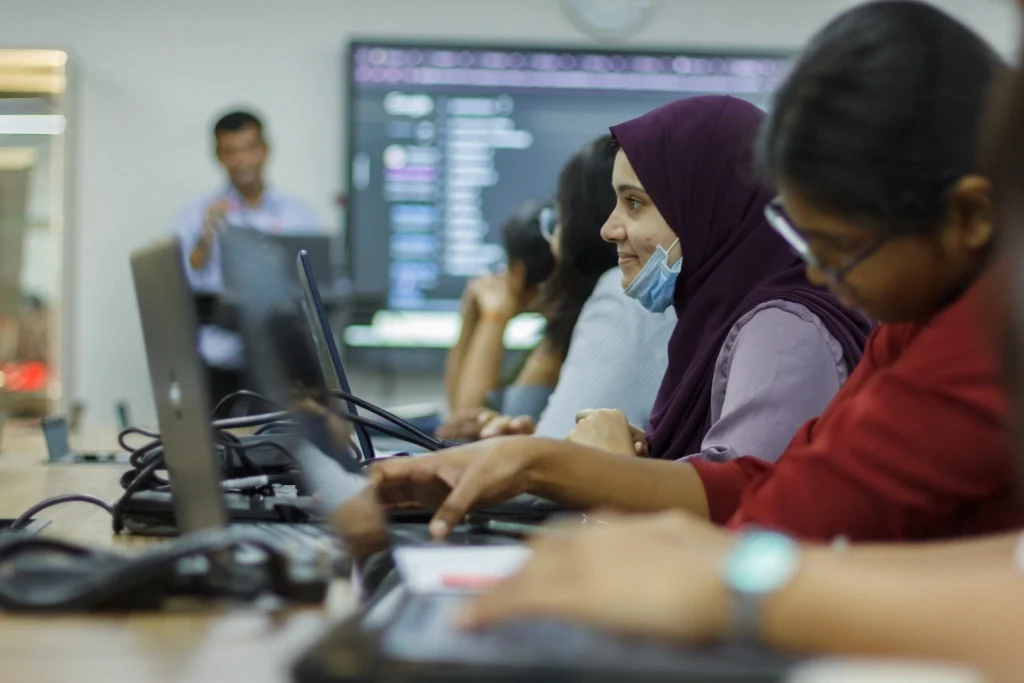
The programme integrates employability training, communication workshop, mock interviews and technical bootcamps to bridge the gap between academic learning and professional readiness. Collaborations with private sector provide internships, mentorships and industry projects that allow aspiring engineers, particularly young women, to gain practical exposure and workplace discipline. This approach nurtures confidence and prepares them to transition seamlessly from classrooms to careers.
For over two decades, Smile Foundation has worked closely with grassroots communities across India, witnessing first-hand the transformative power of targeted interventions. Each initiative, no matter how small, has shown that when opportunity meets access, change becomes inevitable.
In line with the theme of World Science Day 2025, which celebrates the power of science to trust, transform and build tomorrow, Smile Foundation believes that making science truly accessible to all is the first step towards equitable and inclusive education in India.
Spreading the Power of Science
Through initiatives such as STEM Labs, children from underserved communities are introduced to hands-on learning in science, technology, engineering and mathematics. These interactive spaces ignite curiosity and creativity, allowing young learners to explore scientific ideas through practical experience rather than rote learning. Such exposure helps them see science not as an abstract subject, but as a living, breathing part of everyday life something that they, too, can master and shape.
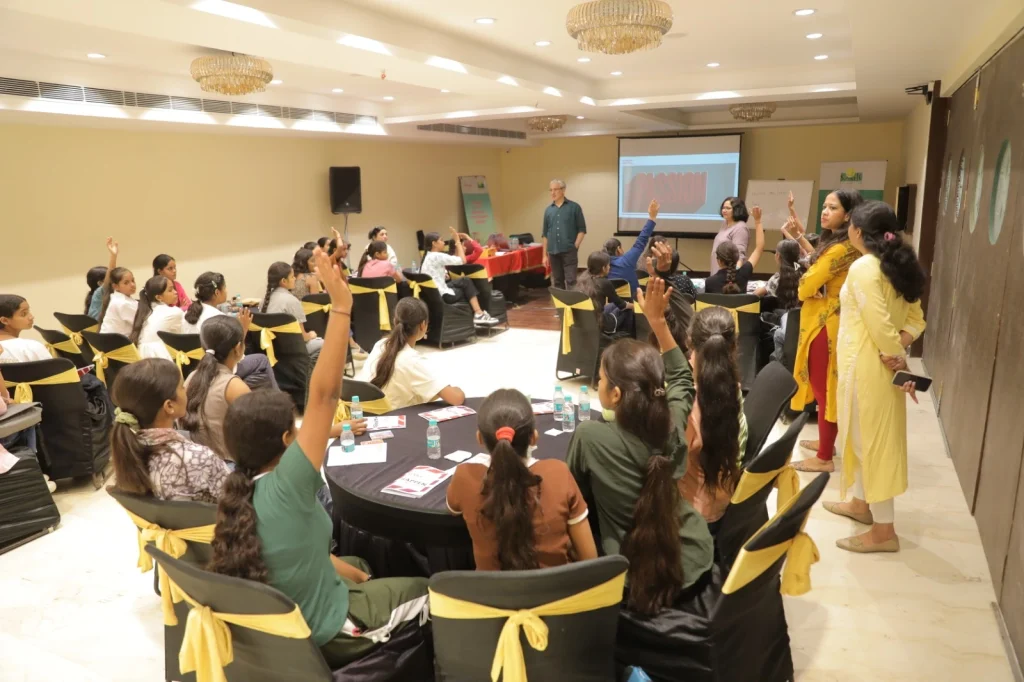

Equally important are scholarships for girls in engineering, which go beyond financial support. They provide what Smile calls “wraparound support” with mentorship, employability training, and guidance that help young women navigate both their studies and future careers. For many, this is the only bridge between aspiration and achievement. It gives them the freedom to dream without the weight of financial pressure and the confidence to step into spaces where women have been historically underrepresented.
The World Science Day for Peace and Development 2025 carries a clear and urgent message: science and innovation must become the tools that create equitable systems of learning and livelihood. By empowering every child through STEM education and supporting India’s daughters in engineering, we are nurturing a generation ready to trust in their abilities, transform their communities and shape a sustainable tomorrow for themselves and for the nation.
Sources: