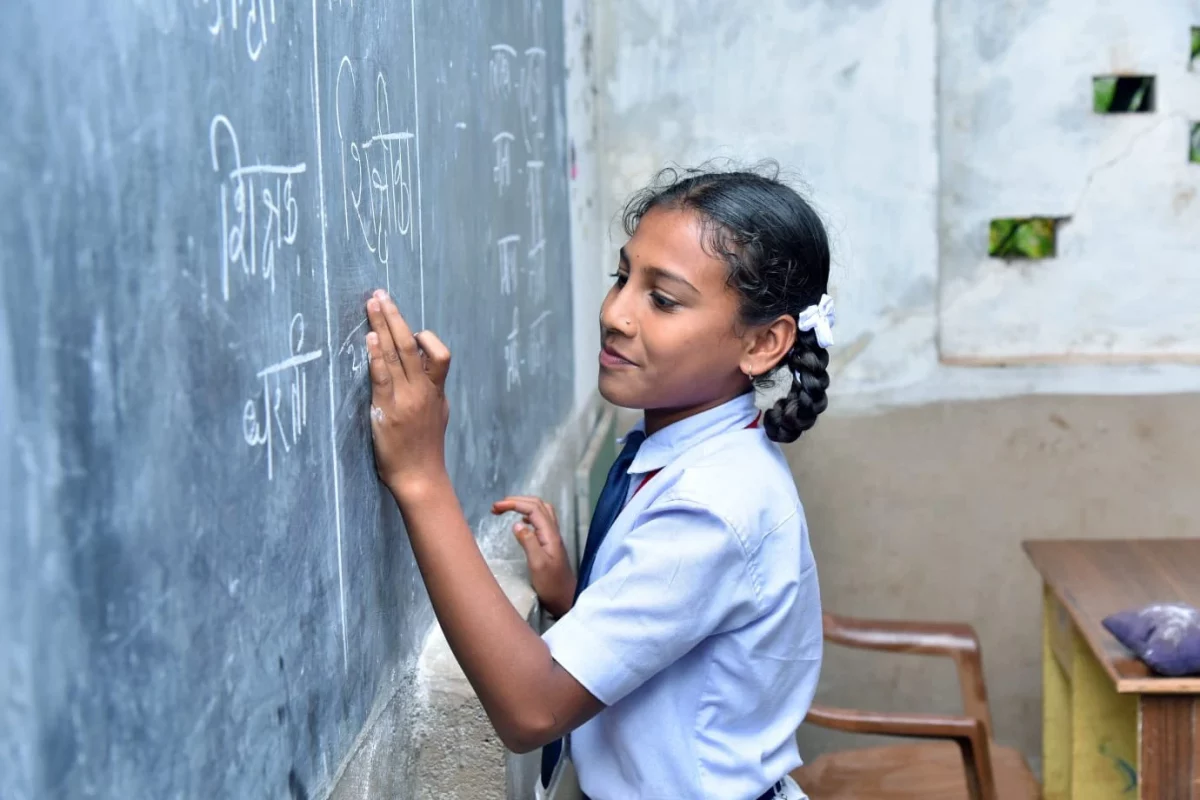In a quiet classroom in Odisha, a girl named Shalini stood up to answer a question. She had no idea her life was about to change. A red stain on her seat, a marker of her first period, brought giggles, whispers, and then silence. No one had told her what menstruation was. She thought she was ill. The next day, overwhelmed by shame, she begged her parents not to send her back to school. And just like that, the promise of a brighter future began to fade.
Shalini’s story is not unique. Across rural India, girls face a combination of stigma, silence, and inaccessibility when it comes to managing their periods. Without awareness, proper facilities, or access to sanitary products, many are pushed out of classrooms, losing days of learning and, eventually, the opportunity for a better future.

UNICEF & WATERAID INDIA STUDY (2015)*
The unspoken numbers
According to UNICEF India, over 253 million adolescents live in India, with nearly half being girls and 25% of them in rural areas. Despite several government-led menstrual hygiene initiatives, thousands of girls still drop out of school due to shame, pain, poor access to products, and lack of supportive infrastructure.
A qualitative study in six Delhi government schools found that around 40% of girls missed school during menstruation owing to menstrual pain, fear of staining, and restrictive social norms.

Period absenteeism-why?
Whether in rural villages or urban neighbourhoods, a girl’s first period often arrives unannounced and with fear. Her body undergoes unfamiliar changes, but in the absence of support and information, this moment becomes isolating. When compounded by poor infrastructure, stigma, and silence, menstruation becomes not just a personal struggle, but an educational barrier.
- Social taboos
Even today, in many parts of India, menstruating girls and women are subjected to regressive restrictions like being barred from entering temples, kitchens, or even touching food on the grounds of being “impure.” These practices are reinforced by harmful myths, such as the belief that menstrual blood is toxic or that using sanitary pads causes infertility. As a result, many girls are pushed toward using cloth or other unhygienic alternatives compromising their health, dignity, and confidence.
- Poor menstrual product access
In many rural communities, girls face limited access to safe menstrual products, clean cloth. or private drying spaces. Adding to their troubles is the issue of no proper disposal facilities; they often resort to using ashes or rags as quiet acts of desperation that compromise their health and dignity.
Menstrual hygiene in Indian women (15-24yrs)
Recent data reflects encouraging progress: 78% of women in India now use hygienic menstrual methods such as sanitary napkins, tampons, or menstrual cups indicating growing awareness and improved access. However, among adolescent girls, only 42% rely exclusively on these hygienic practices*, with significant disparities persisting across states and districts. This gap underscores the urgent need for targeted interventions that address both availability and cultural barriers in underserved regions.
Menstrual hygiene practices among adolescent women in rural India: a cross-sectional study
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9675161
- Paying the hidden cost of secrecy and infrastructure gaps
Many girls across rural India navigate their periods in secrecy by hiding pads in books, fearing stains, missing school events, and sometimes their yearly reviews as well because of menstruation. With no dustbins, running water, or private toilets in schools, managing menstrual hygiene becomes near impossible. The result is a deafening mix of isolation, shame, and lost days of learning.
Menstrual health is a national priority
India has taken steps in the right direction. The Menstrual Hygiene Scheme (MHS), by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, offers subsidised sanitary napkins and peer counselling through ASHA workers. The Rashtriya Kishor Swasthya Karyakram (RKSK) promotes adolescent health, including menstrual awareness. The Suvidha Scheme by the Ministry of Chemicals and Fertilisers introduced biodegradable sanitary pads at ₹1, increasing affordability.
Yet gaps persist. Many of these programmes struggle to reach India’s most marginalised girls. Product availability doesn’t always translate to product use, especially when surrounded by silence and stigma.
As a result, many adolescent girls navigate menstruation in isolation—confused, unprepared, and unsupported. For countless girls, this social conditioning leads to school absenteeism, diminishing their confidence, academic continuity, and long-term opportunities.
Addressing the gaps through strategic partnerships
To bridge these challenges, strategic CSR–NGO partnerships are serving as catalytic agents. By combining grassroots reach with corporate scale, these collaborations have the potential to advance menstrual hygiene management as a systemic solution driving health equity, school retention, and long-term social impact for adolescent girls across India.
Improving school infrastructure beyond brick and mortar
One major challenge for school girls from rural communities during menstruation is the lack of functional school infrastructure; poor washrooms, inadequate disposal, limited water, and no privacy often lead to school dropouts.
What can be done
- Support the development of gender sensitive washrooms with lockable doors, running water, disposable bins and incinerators.
- By partnering with NGOs, corporates can implement their CSR goals for women empowerment. Through impact dashboards, the projects can be tracked to identify the usage, maintenance, and overall the hygienic parameters required for young girls in home and schools.
Culture stigma needs community solutions
One of the most important issues that must be addressed immediately at a large scale is the lack of awareness about menstrual health amongst young girls and their communities. This becomes more concerning when the concerns of young girls are silenced due to vulture silence, shame, and myths that often lead to fear, poor hygiene, and isolation.
What can be done
Corporates can support community based menstrual literacy programmes where they can collaborate with local organisations, ASHA workers and peer educators to increase awareness on menstrual hygiene. Furthermore, they can also educate the girls, teachers and community workers through culturally adapted IEC tools (flipbooks, comics, digital stories ) to challenge taboos and normalise conversations.
Take the example of Shivani. Once hesitant and withdrawn, she found her footing through menstrual health sessions conducted by Smile Foundation’s Swabhiman programme. With accurate information and support, she gained not only knowledge, but also the confidence to speak up. Today, she serves as a peer educator empowering other adolescent girls in her community and promoting health-seeking behaviour.
As part of its integrated approach to women’s health, Smile Foundation’s Swabhiman trains community-based volunteers as reproductive and menstrual health educators in underserved areas. This capacity-building intervention strategically addresses knowledge gaps, dismantles cultural taboos, and promotes safe menstrual hygiene practices directly reducing school absenteeism and health risks among adolescent girls. By embedding peer-led advocacy into last-mile delivery, the initiative strengthens behavioural change at the community level while aligning with national adolescent health goals and SDG targets.
Making innovation accessible, affordable, and adaptable
As key drivers of social impact, CSR–NGO partnerships are well positioned to eliminate unhygienic menstrual practices such as the use of cloth, ash, or sacks by co-developing and scaling access to affordable sanitary products tailored for rural adolescent girls. In light of growing environmental concerns, these partnerships must also prioritise innovation in biodegradable and reusable menstrual solutions, ensuring both adolescent health and ecological sustainability. Such an approach aligns with ESG goals and supports long-term, community-based health equity.
What can be done
- Support women-led production units for biodegradable sanitary napkins or menstrual cups.
- Collaborate on last mile distribution through workshops in local communities and schools, Anganwadis and frontline health workers.
For instance, through targeted workshops on menstrual hygiene, Smile Foundation’s Swabhiman programme ensures last-mile delivery of accurate, stigma-free education to adolescent girls in underserved communities. By promoting body literacy and safe hygiene practices, the initiative empowers girls with the confidence to stay in school, safeguard their health, and become agents of change in their communities.
- Support impact evaluations to track product adoption, usage frequency, and behavioural shifts.

Her better health and future with Swabhiman
Swabhiman addresses menstrual hygiene as a critical enabler of uninterrupted education for adolescent girls in rural India. By training peer educators, frontline volunteers, and community health workers, Swabhiman delivers accurate, stigma-free menstrual literacy at the grassroots. It also facilitates access to sanitary products, promotes hygienic practices, and advocates for safe, girl-friendly school sanitation infrastructure. This integrated approach reduces absenteeism and school dropouts caused by menstruation-related challenges. Aligned with national priorities and SDGs 4 and 5, Swabhiman empowers girls to manage menstruation with dignity transforming it from a source of shame into a gateway for continued learning and confidence.
A call to strategic CSR for menstrual hygiene in India
By investing in menstrual health, CSR initiatives can move the needle on multiple fronts including school attendance, public health, gender empowerment, and community resilience.
Smile Foundation invites partners committed to building inclusive, lasting impact. Let’s work together so that menstruation is no longer a reason for any girl to drop out but a moment where she steps into knowledge, dignity, and power.