A youthful nation like ours must leave an impact on the entire world, said our Head of the State. With over 68% of India’s population residing in rural areas, the need to harness this demographic dividend through upskilling is more pressing than ever.
For rural youth, this means acquiring skills that are relevant to the evolving job market and the specific needs of their communities. As agriculture undergoes a transformation, with many farmers transitioning to non-farming jobs, upskilling becomes important for those seeking alternative employment opportunities. We are also hoping that with better incentives, there will come a generation of modern farmers who lead our agricultural potential.
Upskilling rural youth is not just about enhancing employability- it’s about fostering a generation that can contribute to the economic, social and environmental sustainability of their communities.
The rural youth in India face a unique set of challenges. Limited access to quality education, lack of exposure to diverse career paths and the traditional reliance on agriculture for livelihoods have often kept them from realizing their full potential.
With the reports predicting about 50% of the population residing in urban areas by 2047, it becomes an alarming threat toward the agrarian crisis with the increase in migration and shift to non-farming jobs for better opportunities.
Shift to Non-Farming Jobs and Migration
Rural youth are increasingly choosing non-agricultural jobs due to a variety of factors. These factors contribute to a shift in employment patterns, with rural youth seeking opportunities that promise better economic and social outcomes. Major reasons include-
- Educational aspirations for better education that offers more stable and higher incomes.
- The allure of urban life and white-collar jobs seems to be more prestigious and rewarding.
- Non-agricultural jobs tend to provide regular and assured income compared to uncertainties of farming, especially true due to the effects of climate change.
- Rising opportunities for more non-farm employment in urban areas due to improved infrastructure and industrialisation attract rural youth.
Most importantly myriad challenges farmers face that impact their productivity and livelihoods act as the biggest discouragement to the youth to move towards non-farming jobs and migrate to urban areas. A few major issues include-
- Limited access to credit to adopt new technologies and crop diversification.
- Lack of proper marketing channels price fluctuations in the market.
- Inadequate insurance coverage to protect small farmers against crop failures.
- Lack of capacity-building programmes for farmers to equip them with modern agricultural practices and equipment.
- Small-size land holdings and Inadequate availability of irrigation water make them dependent on monsoon rains.
Specialized Training is required to make agriculture aspiring youth
- Develop opportunities like Agri-tourism and showcase success stories of young farmers to serve as inspiration and role models.
- Training in sustainable and organic farming methods and introducing youth to the latest agricultural technologies such as farm management software, precision farming, drones, etc. can make it more tech-oriented and appealing.
- Courses on Agri-Entrepreneurship can teach farm management, agricultural marketing and finance, which can empower youth to see farming as a viable business venture.
- Specialised training in horticulture and floriculture can open up opportunities in landscaping, nursery management, etc.
- Vocational training in Dairy and Poultry Farming, Fisheries and Aquaculture can help diversify income sources.
- Skills in food processing, packaging and preservation can lead to opportunities in the growing food industry.
- Technical courses on the operation and maintenance of farm machinery can lead to employment in the agricultural equipment sector.
- Skills in inefficient water use and irrigation systems are critical for sustainable agriculture and can offer specialised career paths.
Strategic ways to create better opportunities for upskilling rural youth
Identify in-demand non-agricultural skills in the local job market and map them against the current skill levels of the rural youth.
- Establish vocational training centers to provide practical, hands-on training that aligns with industry standards.
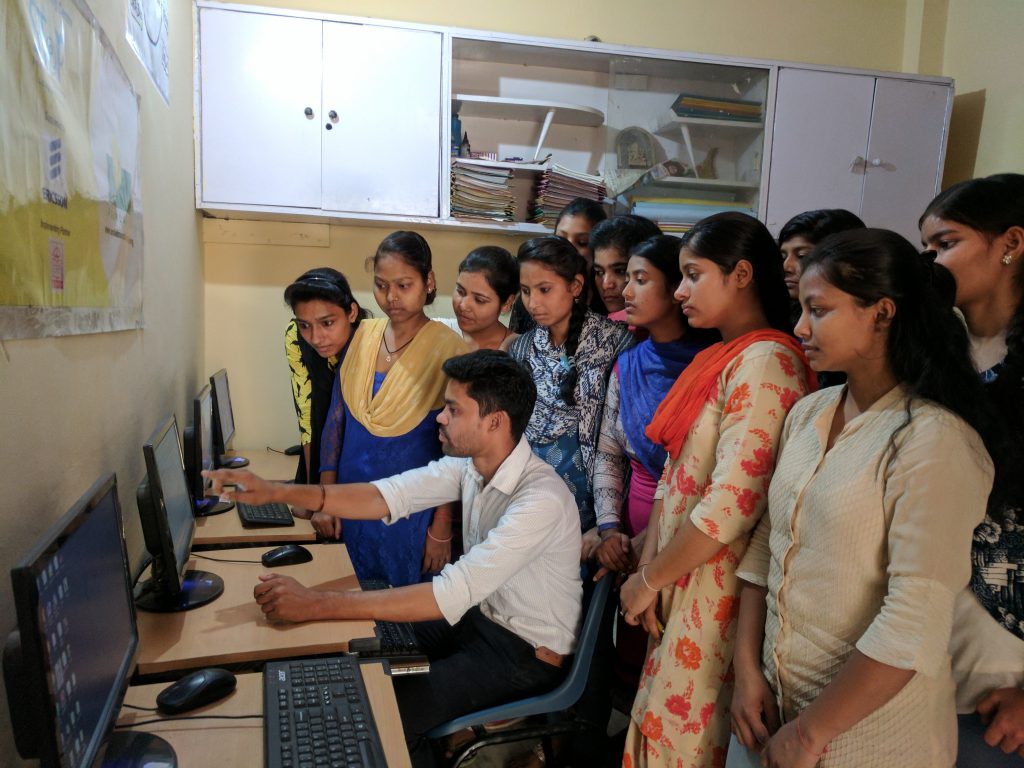
- Implement digital literacy programs to ensure that rural youth are comfortable with technology.
- Foster public-private partnerships to create apprenticeship and internship opportunities and promote entrepreneurship.
- Improve infrastructure in rural areas, such as transportation and internet connectivity, and organize networking events that connect rural youth with industry professionals.
- Facilitate access to finance for rural youth, leverage government initiatives, and advocate policies to support rural youth.
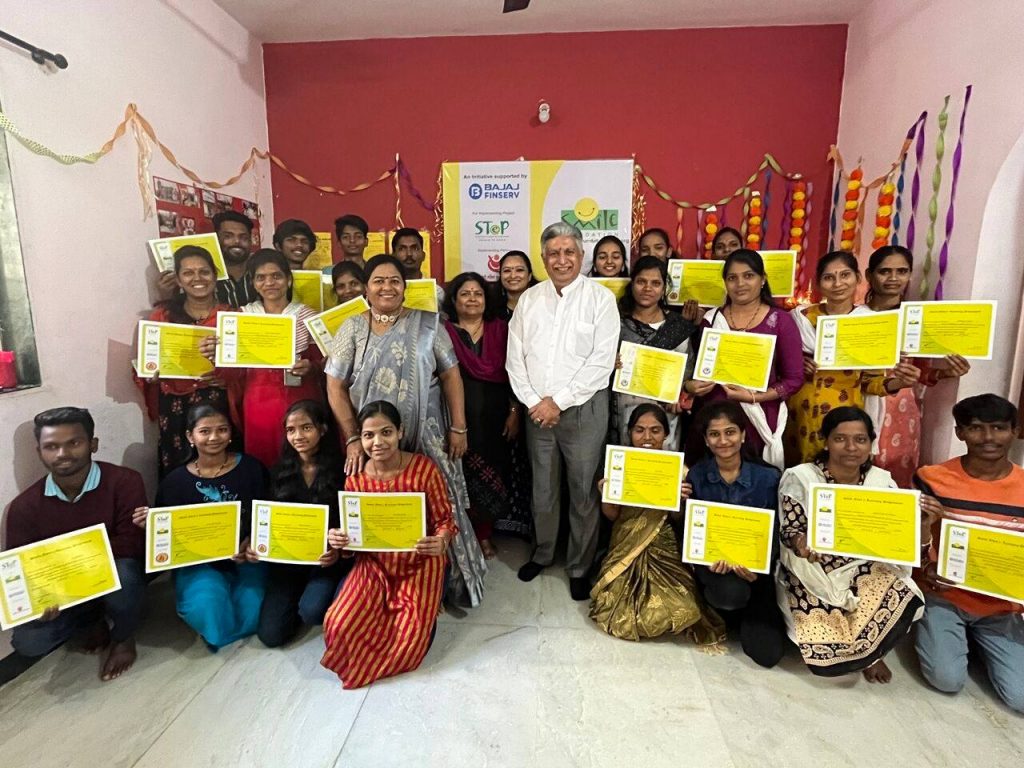
Development Organisations upskilling the Indian youth
Development organisations like Smile Foundation play a significant role in upskilling youth. This is especially true for areas where government programmes need strengthening with active convergences. We tailor training programmes relevant to the local youth, depending on the job market. By providing learning resources and tools through partnerships, we bridge the gap between skills and resources. This helps them navigate career paths and connect them to potential employers.
A few programmes and initiatives of Smile Foundation to upskill rural youth are as follows-
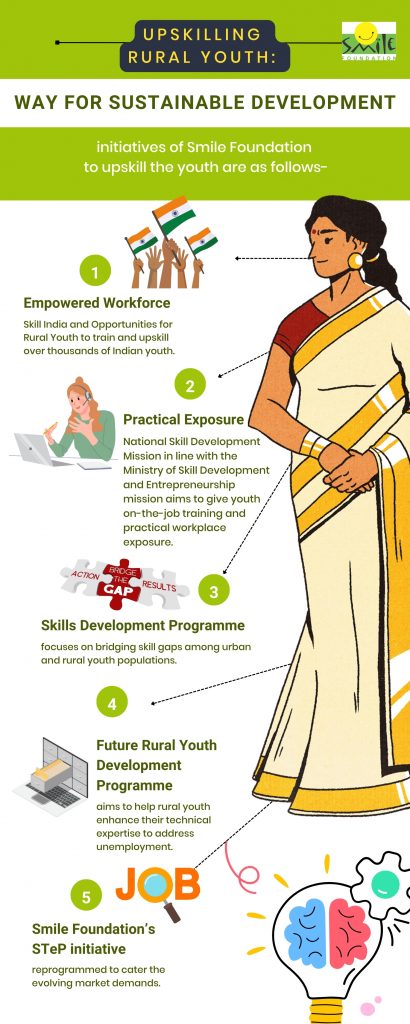
Upskilling rural youth is an educational, social and economic imperative. It can lead to personal growth, economic empowerment and community development.
While the path to upskilling rural youth is laden with challenges, it also presents immense opportunities. The key lies in tailoring education to meet the technical and life skills required in rural areas. Collaboration between NGOs and the private sector is essential to create a sustainable ecosystem for skill development.









