In June, a class XII student from Uttar Pradesh’s Barabanki district, Pooja, participated in Japan’s prestigious Sakura Science High School Programme. Pooja invented a dust-free thresher that blocks agricultural dust emitted from wheat farms and provides clean air. The daughter of a labourer, Pooja is the only participant from UP to participate in the programme organised by the Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST). Despite her humble background, she had a breakthrough in her invention when she was in class VIII itself. She received both state and national recognition under INSPIRE awards. This is the actual power of STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics). Pooja is an ideal example of how STEM labs are nurturing creativity, critical thinking, and innovation among students.
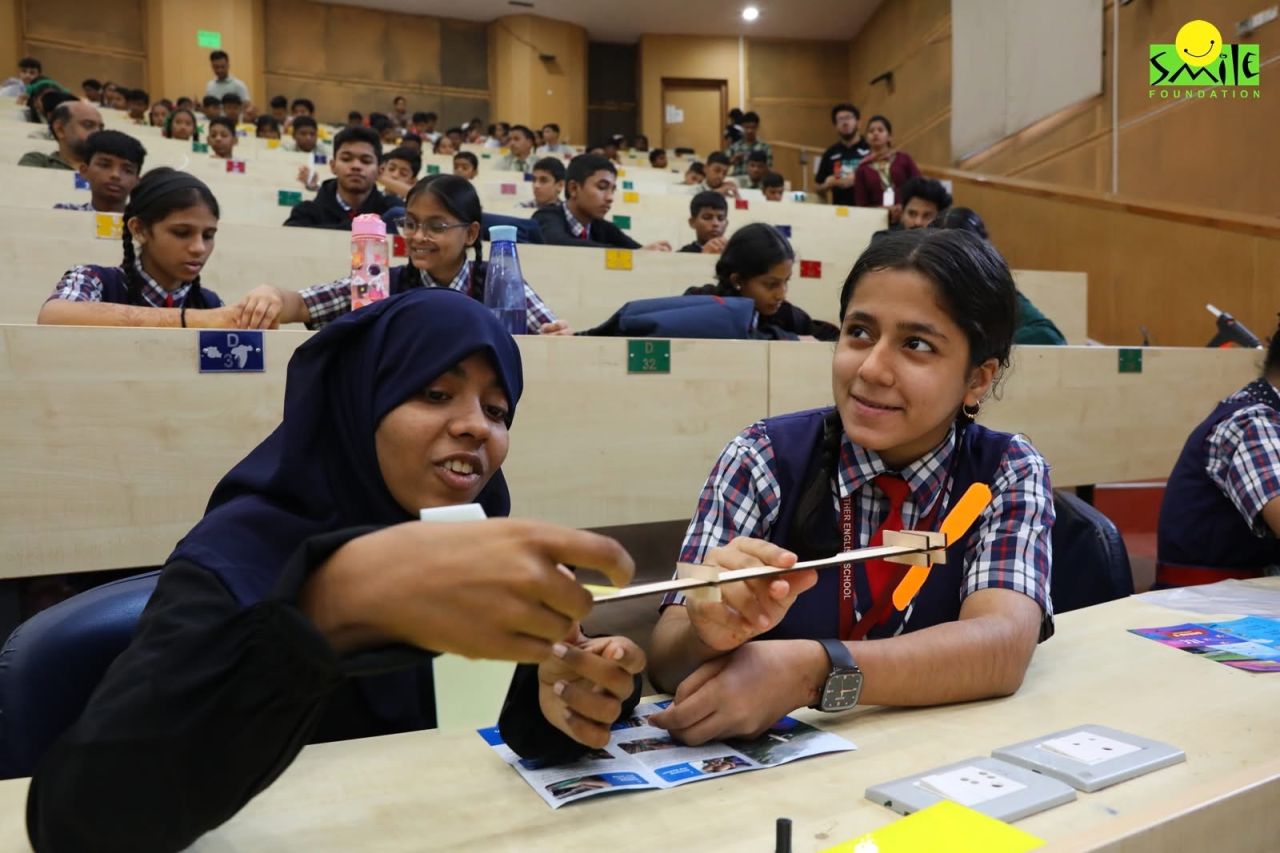
Walk into a modern STEM lab in any progressive Indian school and you won’t find rows of silent desks or rote memorisation. Instead, you’ll see students huddled around 3D printers, experimenting with circuits, or programming miniature robots to navigate a maze. STEM labs are reimagining what education looks like in the 21st century, turning passive learning into active exploration.
In times where the future of work is being shaped by artificial intelligence, automation, and technological disruption, the traditional education model no longer suffices. India needs a generation of thinkers, builders, and problem-solvers—skills that cannot be taught through textbooks alone. This is where STEM labs come in. These dynamic, hands-on environments foster creativity, critical thinking, and real-world application, positioning students not just to adapt to the future but to shape it.
The promise of a STEM lab
A STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, Mathematics) lab is a dynamic, hands-on learning environment that rewards curiosity, collaboration, and real-world problem-solving. Unlike traditional classrooms, which often emphasise rote learning, STEM labs allow students to build, test, code, and experiment—providing a tangible connection between theory and application. This approach cultivates critical 21st-century skills, including innovation, analytical thinking, and teamwork.
These spaces more than hubs of scientific explorations are incubators of confidence. Children are writing algorithms, building robots, and simulating climate models. This interdisciplinary framework helps young learners see how knowledge converges to shape the world around them.
Coding: The new literacy
In today’s AI-driven world, coding is no longer a niche skill; it is foundational. Like reading and writing, coding enables people to make sense of their environment—in this case, the digital environment. Whether it’s writing a basic Python script, debugging a web app, or using Scratch to animate a story, coding gives students the ability to think in structured, logical ways.
More importantly, learning to code early in life helps demystify technology. AI may be writing code, but humans are still steering its purpose and ethics. When taught in a STEM lab setting, coding becomes a tool for creativity and exploration. Students apply their logic to build games, control sensors, or automate models, receiving instant feedback that sharpens their skills. The result is a generation of learners who don’t fear technology but shape it.
Robotics: Engineering in motion
If coding is the brain, robotics is the body. Robotics education represents the seamless integration of mechanical engineering, electronics, and computer programming. It translates abstract STEM concepts into real-world functions. From automating agriculture to managing warehouse logistics and even conducting surgeries, robotics is revolutionising industries.
In STEM labs, students assemble kits, program microcontrollers, and troubleshoot movement sequences. These activities teach resilience, systems thinking, and real-time problem-solving. As students see their robotic creations perform tasks, it not only boosts their technical knowledge but also their confidence to innovate. In effect, they learn how technology can serve humanity’s evolving needs.
Curiosity: The engine of discovery
At the heart of any STEM education initiative lies curiosity. The freedom to ask “What if?” and “Why not?” is what separates passive learners from innovators. STEM labs encourage inquiry-led learning, where mistakes are seen as steps toward discovery. This openness fosters grit and a love for experimentation—two qualities vital for both academic and personal growth.
In such an environment, students learn to view challenges as puzzles and develop the capacity to iterate solutions. Whether they’re 3D-printing bridge models, designing solar cars, or programming AI chatbots, the emphasis is on learning by doing. STEM labs thus lay the psychological groundwork for entrepreneurship, scientific inquiry, and ethical leadership.
Government push for STEM: Policy backing innovation
Recognising the power of STEM, the Indian government has launched several impactful initiatives:
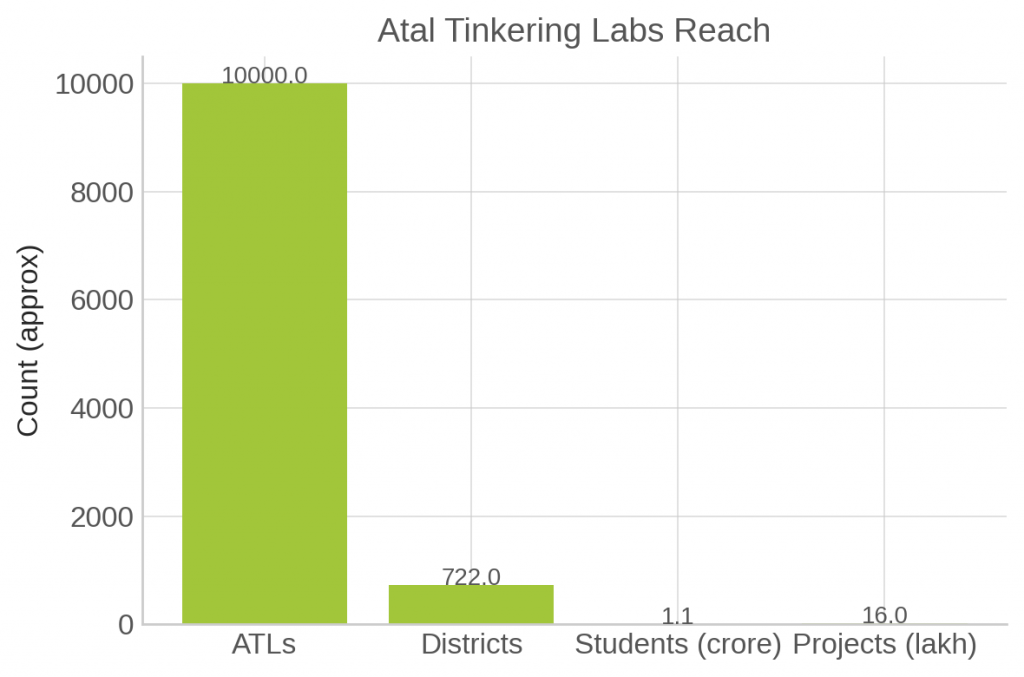
Atal Tinkering Labs (ATLs): Over 10,000 labs across 722 districts have been set up under the Atal Innovation Mission, reaching 1.1 crore students and leading to over 16 lakh innovation projects. These labs focus on 21st-century skills like design thinking, ethical leadership, and collaboration.
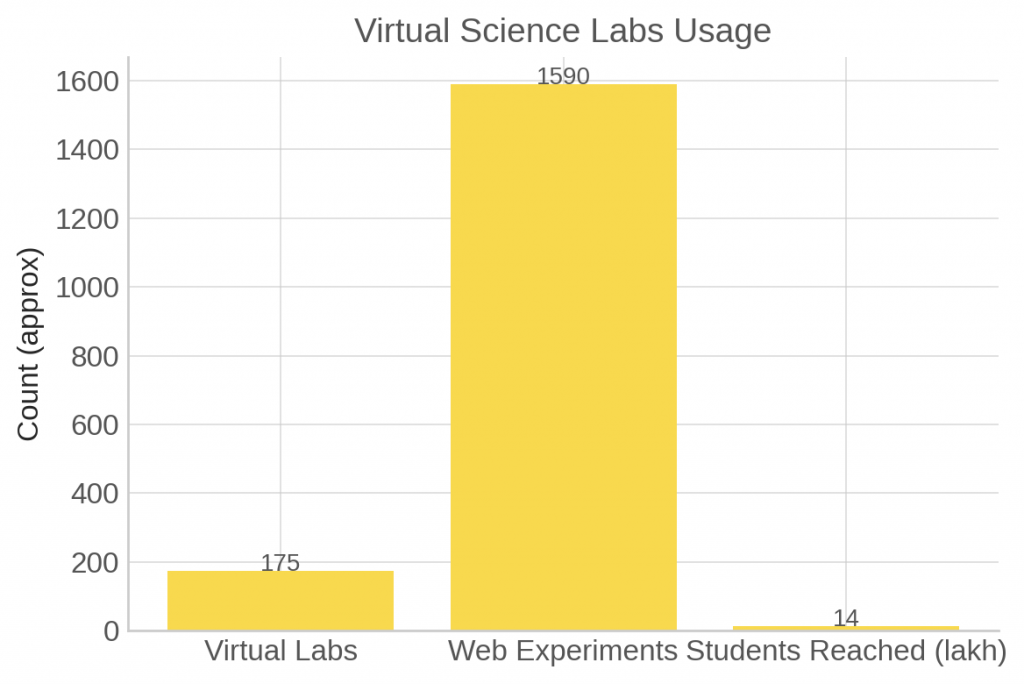
Virtual Science Labs (CSIR Jigyasa): Launched in 2021, this initiative offers 1,590+ web-enabled experiments across disciplines such as biotechnology, electronics, and physical sciences. Over 14 lakh students have accessed these labs, democratising scientific research exposure.
These initiatives reflect a systemic shift in India’s education policy, from content-heavy curricula to curiosity-driven learning.
Smile Foundation’s contribution
While policy drives scale, implementation on the ground requires trusted partners. Smile Foundation has been at the forefront of democratising STEM education, especially for underserved communities.
In 2025, Smile Foundation partnered with BMW India Foundation to launch an ambitious STEM programme across government-aided and community schools in Delhi. The initiative is projected to reach over 2,500 students annually through:
- State-of-the-art STEM labs with digital tools, robotic kits, and testing devices
- A “STEM on Wheels” mobile lab for outreach to marginalised communities
- Workshops, science fairs, and teacher training to ensure sustainability
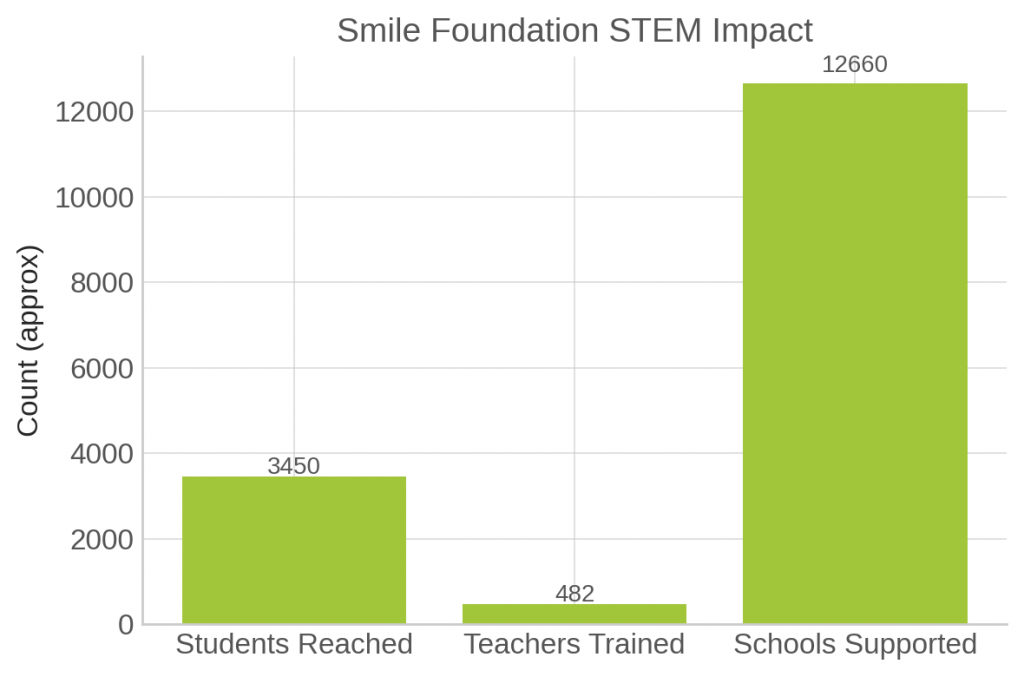
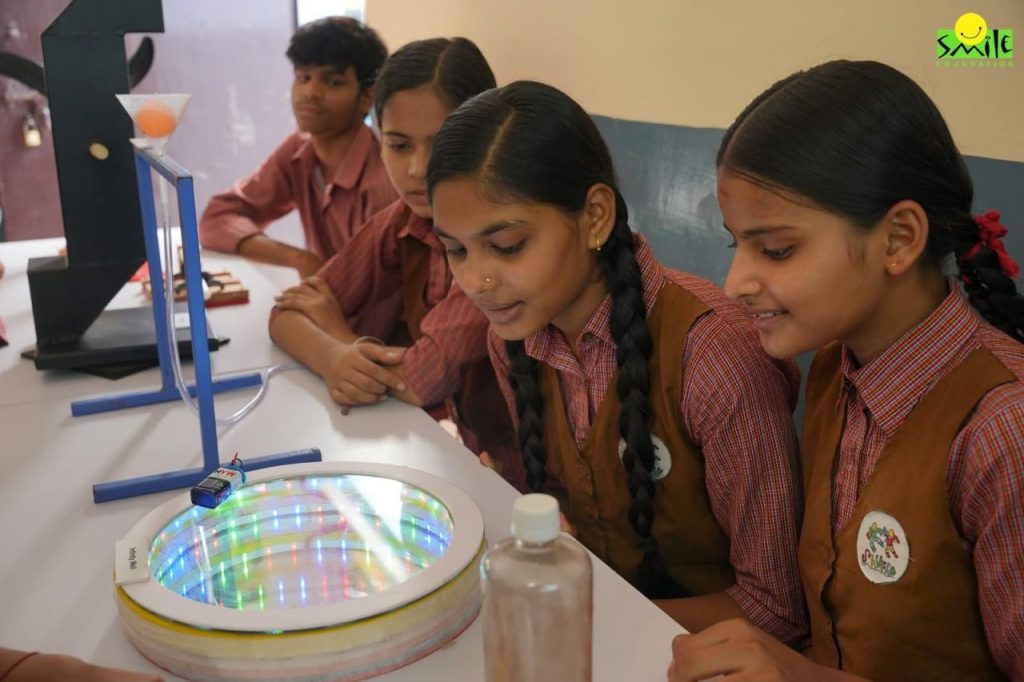
Additionally, their collaboration with IIT Bombay in 2024 brought advanced STEM modules to over 950 students in fields like astronomy, aero-modelling, and 3D printing. This high-touch model, reinforced by their flagship Mission Education programme, has created vibrant learning spaces where critical thinking and creativity are at the core.

To ensure these innovations are embedded into daily teaching, Smile Foundation has trained 482 teachers and 116 school leaders through over 86 workshops. Covering everything from pedagogy to foundational numeracy, these sessions empower educators to make classrooms interactive, inquiry-led, and future-focused. As of 2024, the foundation has supported over 12,660 government schools in 15 states.
What lies ahead: Scaling impact
India’s STEM future rests on how effectively it can scale such interventions. The goal is not just to create coders or roboticists but to cultivate problem-solvers and ethical technologists. For this, a multi-pronged approach is needed:
- Public-private partnerships: Scaling high-quality STEM labs requires investment, expertise, and local understanding. Collaborations like that of Smile Foundation and BMW India Foundation set a strong precedent.
- Curriculum integration: STEM must not remain an after-school activity. It needs to be embedded into mainstream curricula, aligned with national education goals like NEP 2020.
- Gender inclusion: STEM must actively dismantle gender biases. This means inclusive innovation clubs, mentorship for girls, and culturally rooted interventions.
- Capacity building: Teachers remain the cornerstone. Ongoing training, mentorship, and performance support must be prioritised to sustain quality.
- Tech accessibility: With emerging tools like AI, AR/VR, and IoT entering classrooms, infrastructure and digital equity need urgent attention to avoid deepening the education divide.
A well-equipped STEM lab is a mindset incubator. In such spaces, children learn to question, design, fail, and try again. They understand that science is not a set of answers but a method of asking better questions. India’s investment in STEM labs, when combined with inclusive implementation models like Smile Foundation’s, holds the potential to turn its vast demographic dividend into a generation of innovators and problem-solvers.

As coding becomes the new literacy, robotics the new machinery, and curiosity the new capital, STEM labs stand as India’s gateway to a more equitable, inventive, and empowered future.
Sources